The Industrial Area plays an exceedingly strategic role as an industrial infrastructure in achieving spatial compatibility, industrial dispersion, and environmental sustainability. This is in accordance with the mandate of Article 106 of Law Number 3 of 2014 concerning Industry ("Law No.3/2014"), which imposes the obligation for new industries to be situated within the Industrial Area.
The government, in conjunction with local administrations, continues to exert efforts to foster the development of Industrial Areas, enticing both domestic and foreign investors to venture into these territories. To accomplish this, the government has issued Government Regulation Number 142 of 2015 concerning Industrial Areas ("GR No.142/2015"), specifically focused on Industrial Areas, with the aim of rendering these zones more alluring as prime investment destinations within the industrial sector.
The development of an Industrial Area necessitates fulfilling specific criteria, encompassing technical, economic, environmental, and financial feasibility. Consequently, a guiding framework for the development of the Industrial Area is indispensable, as elucidated in the Technical Guidelines for the Development of Industrial Areas.
Law No. 3/2014 elucidates that an Industrial Area represents a concentrated zone for industrial activities, replete with complementary facilities and infrastructure, meticulously developed and managed by the Industrial Area Corporation.
Enhancing Livability and Sustainability Within Industrial Areas
One of the pivotal supporting facilities is infrastructure, as stipulated in Article 62 Law No./2014. It is accentuated that the industry necessitates the presence of infrastructure facilities that harmonize with the extant spatial planning of the region.
Furthermore, GR No.142/2015 distinguishes between two classifications of infrastructure: industrial infrastructure and supporting infrastructure. One of the elements of supporting infrastructure is housing. This housing infrastructure can be constructed either by the local government or by the Industrial Area Corporation, should residential plots be designated for development within the Industrial Area. GR No.142/2015 further expounds upon the standards applicable to the Industrial Area. Article 44 mandates that the Industrial Area Corporation must adhere to the Industrial Area standards. Compliance with these standards leads to the accreditation of the Industrial Area.
With the existence of standards that must be met by the Industrial Area entrepreneurs, there are also sanctions imposed for non-compliance with the prescribed standards. Article 57 of GR No.142/2015 specifies that the sanctions imposed entail administrative actions in the form of written warnings or administrative fines determined by the Minister, governor, or regent/mayor, in accordance with their respective authority, based on examination results or existing reports.
Technical Guidelines for the Development of Industrial Areas under Minister of Industry Regulation Number 40/M-IND/PER/7/2016 of 2016 on Technical Guidelines for the Development of Industrial Areas.
Land Utilization Pattern
The land utilization pattern for the development of the Industrial Area is as follows:
- The maximum area allocated for industrial plots is 70% of the total land area, inclusive of land allocation for small and medium industries.
- The minimum Green Open Space (Ruang Terbuka Hijau/RTH) should occupy 10% of the total land area.
- Roads and channels should account for approximately 8-12% of the total land area.
- Other fundamental infrastructure and supporting infrastructure should constitute approximately 8-12% of the total land area.
Provisions concerning land utilization for buildings, such as the Building Coverage Coefficient (Koefisien Dasar Bangunan/KDB), Floor Area Ratio (Koefisien Lantai Bangunan/KLB), and Building Setback Line (Garis Sempadan Bangunan/GSB), are regulated in accordance with the applicable regional government regulations.
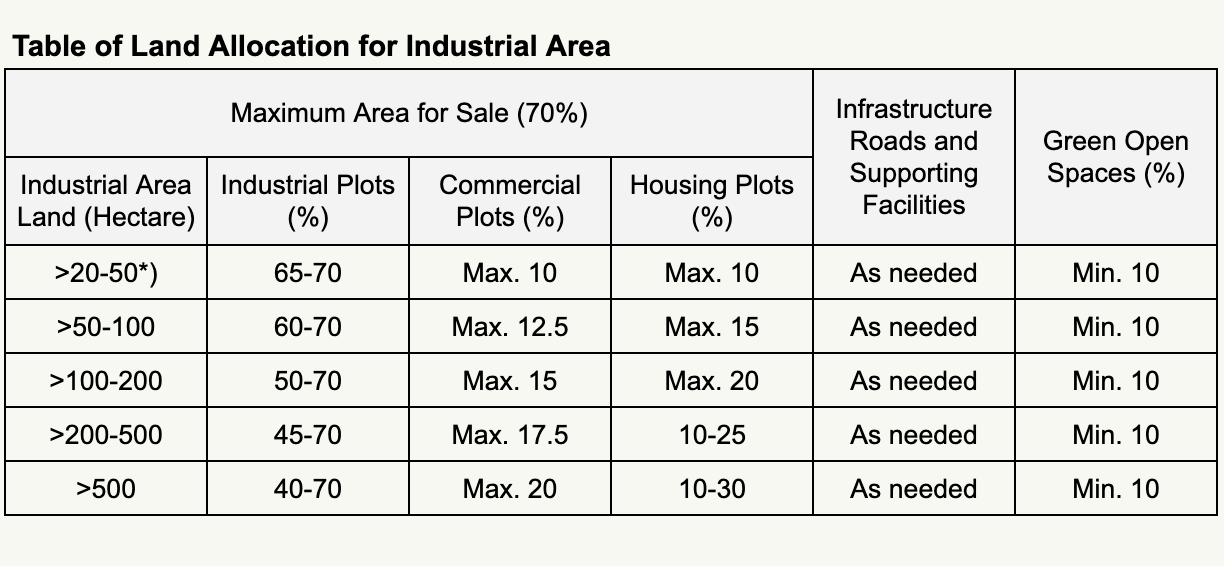
Housing Plots or Residential Plots are parcels of land provided by the Industrial Area Corporation for worker housing, including supporting amenities such as sports areas and places of worship.
If you, a prospective client, have further inquiries about the topic discussed above, Schinder Law Firm is one of the numerous corporate law firms in Indonesia that has handled a myriad of similar matters, with a wealth of experience and a cadre of professional corporate and civil lawyers in its arsenal, rendering it one of the foremost consulting firms in Indonesia. Feel free to contact us at info@schinderlawfirm.com for further consultation.
Author: Budhi Satya Makmur